Understanding Business Intelligence: An Overview
Business Intelligence (BI) refers to the strategies and technologies employed by enterprises for the data analysis of business information. BI encompasses various processes, including data collection, data analysis, and data visualization, aimed at transforming raw data into meaningful insights. These insights are crucial for making informed business decisions, enhancing operational efficiency, and gaining a competitive edge in the market.
At the core of BI is data collection, which involves gathering information from various sources such as databases, spreadsheets, and external data providers. This data is then cleaned and organized in data warehouses, making it accessible and ready for analysis. Data analysis, the next critical component, employs various techniques and tools to interpret the data, identify patterns, and generate insights. Modern BI has evolved from traditional reporting methods to include advanced analytics and predictive modeling, which provide deeper and more actionable insights.
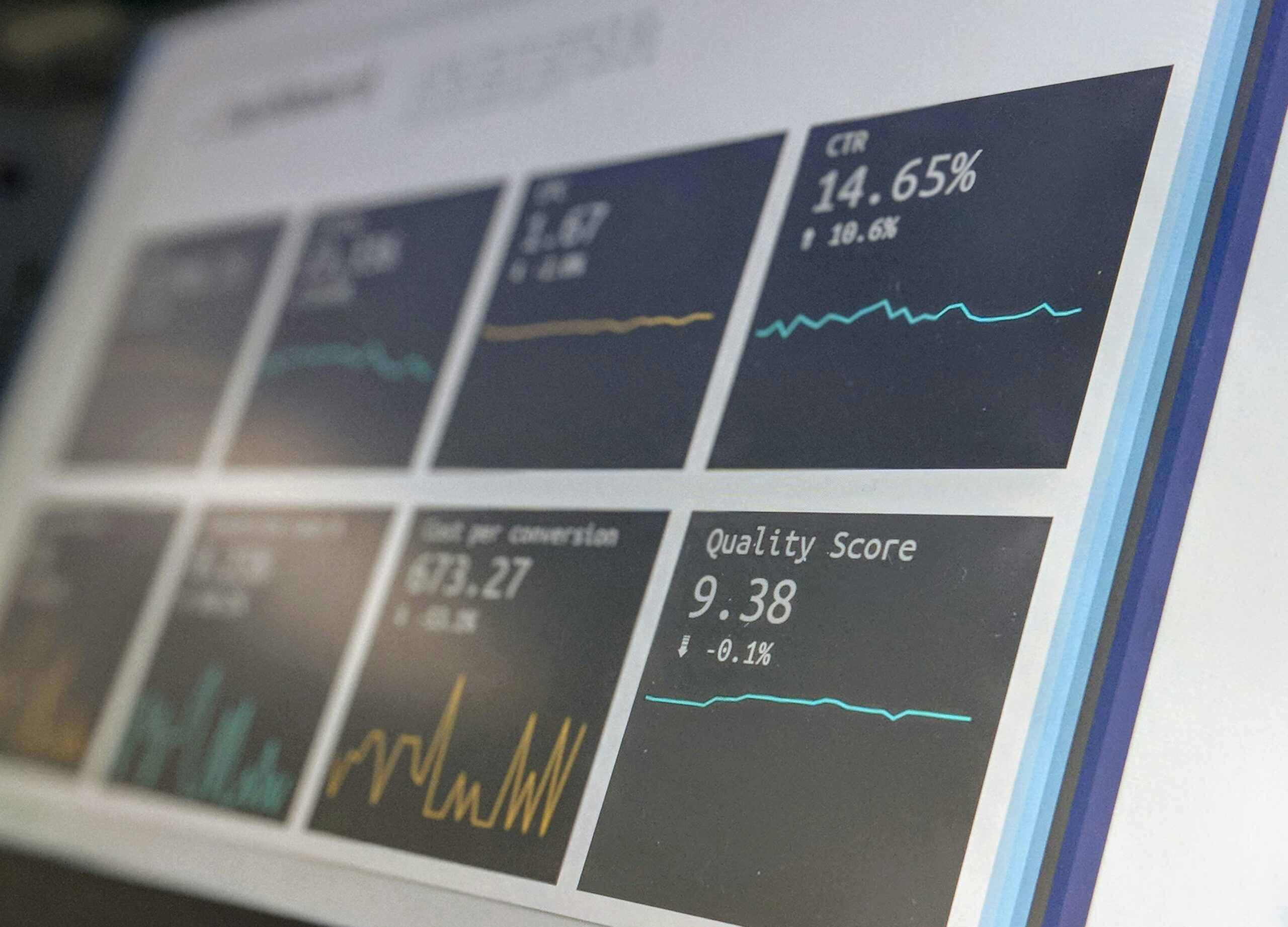
Data visualization is another fundamental aspect of BI, allowing complex data to be represented visually through charts, graphs, and dashboards. These visual tools enable stakeholders to quickly understand trends, anomalies, and performance metrics, facilitating more effective communication and decision-making. Dashboards, in particular, are widely used BI tools that provide real-time data visualization, helping businesses monitor key performance indicators (KPIs) and track progress toward goals.
In addition to dashboards, other essential BI tools include data warehouses, which store large volumes of data in a structured manner, and reporting tools that generate detailed reports and summaries. These tools collectively enhance a company’s ability to make data-driven decisions, optimize operations, and stay ahead of competitors.
The benefits of implementing BI are manifold. Improved decision-making is one of the most significant advantages, as BI enables businesses to base their decisions on factual data rather than intuition. Operational efficiency is also enhanced, as BI tools streamline processes and reduce the time required to analyze data. Furthermore, businesses gain a competitive advantage by leveraging BI to identify market trends, understand customer behavior, and anticipate future opportunities.
Implementing Business Intelligence: Best Practices and Challenges
Implementing Business Intelligence (BI) in an organization is a multifaceted process that requires a strategic approach. The journey begins with defining clear business objectives. Understanding what the organization aims to achieve with BI, whether it is improving decision-making, enhancing operational efficiency, or gaining competitive advantage, sets the foundation for a successful implementation. Once objectives are established, selecting the right BI tools becomes crucial. These tools should align with the organization’s needs and capabilities, ensuring they can handle the data volume and complexity.
Data integration is a critical step in the BI implementation process. It involves consolidating data from various sources into a unified system. This step often poses challenges due to data quality issues, such as inconsistencies, inaccuracies, and duplicates. Establishing a strong data governance framework can mitigate these issues, ensuring data integrity and reliability. Additionally, addressing resistance to change is vital. Employees may be hesitant to adopt new systems, fearing disruption of their workflow. Involving key stakeholders from the beginning and providing comprehensive user training can facilitate smoother transitions and improve user acceptance.
Scalability is another challenge that organizations might face. As the volume of data grows, the BI system must be able to scale efficiently. Planning for scalability from the onset by choosing flexible and robust BI solutions can prevent future bottlenecks. Continuous evaluation and improvement of BI systems are essential to adapt to evolving business needs and technological advancements. Regularly updating the system ensures that it remains relevant and efficient.
Real-world examples highlight the practical benefits of effective BI implementation. For instance, a retail company that integrated BI tools to analyze customer purchasing patterns achieved a significant increase in sales by tailoring their marketing strategies. Similarly, a healthcare provider improved patient care and operational efficiency by leveraging BI to streamline data from various departments.
In summary, the successful implementation of Business Intelligence requires careful planning, addressing potential challenges proactively, and involving all relevant stakeholders. By following best practices such as establishing a strong data governance framework, providing adequate training, and ensuring scalability, organizations can unlock the full potential of BI to drive informed decision-making and achieve their business objectives.

